RECOMMENDED NEWS
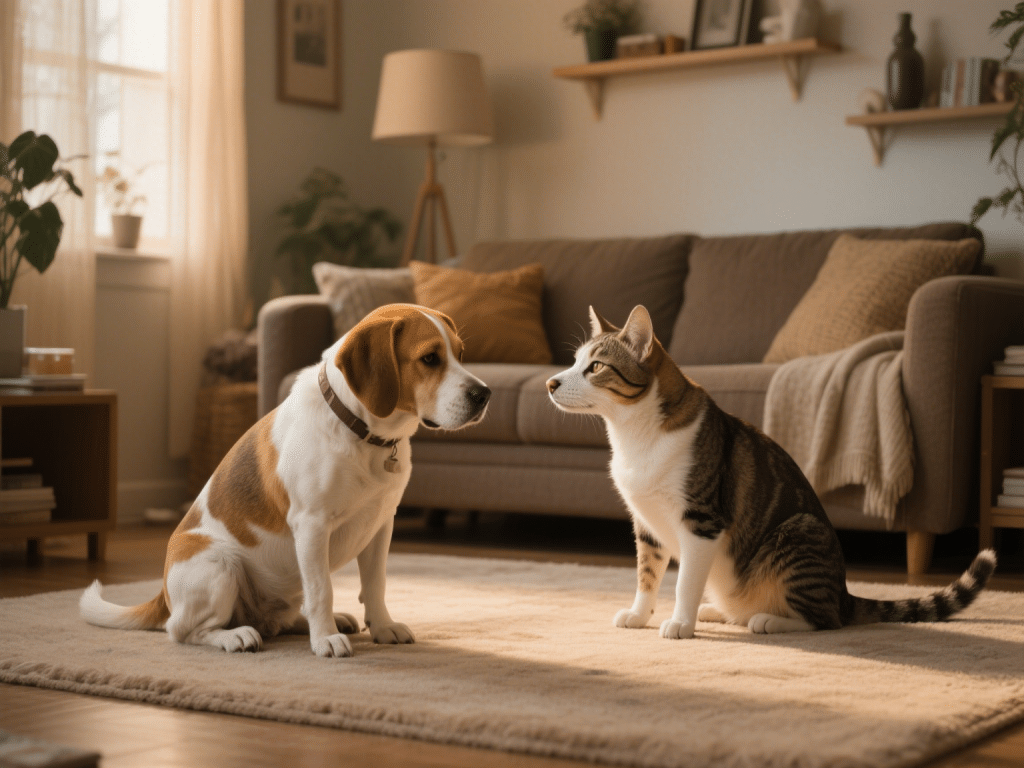

Safe Introduction of New Pets to Resident Animals
Introducing a new animal into a household with established pets can spark anxiety, territorial aggre...
Read More →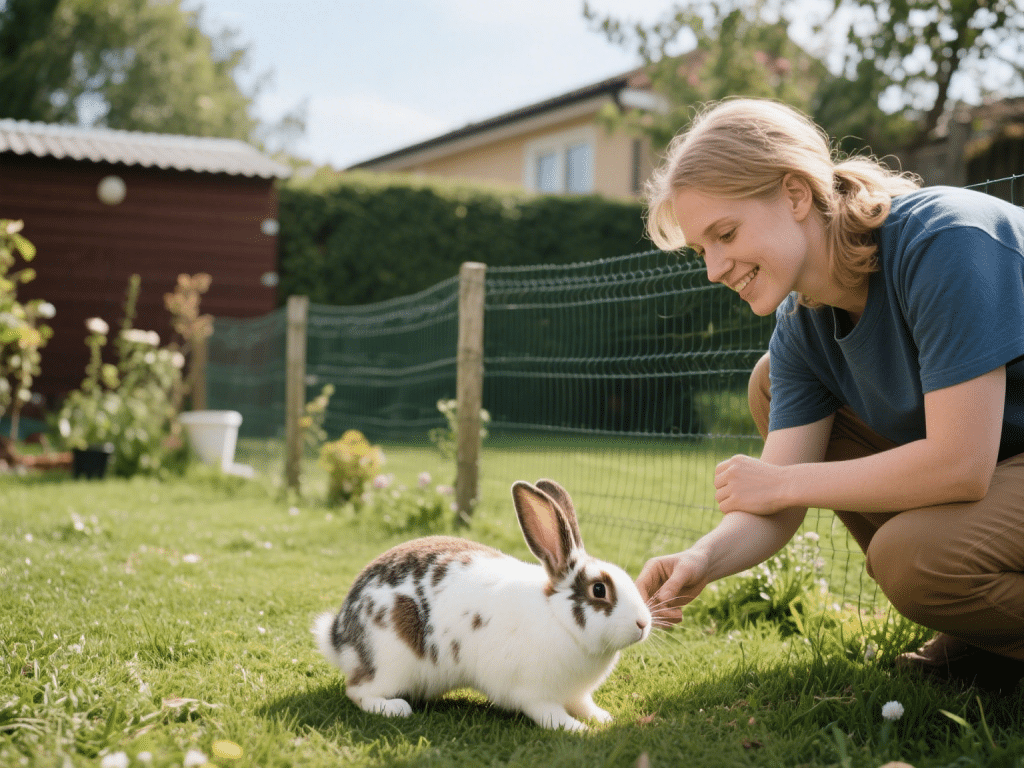
Preventing Obesity in Rabbits: Diet and Exercise Guidelines
Rabbits are prone to weight gain when fed unlimited pellets and housed without adequate space for mo...
Read More →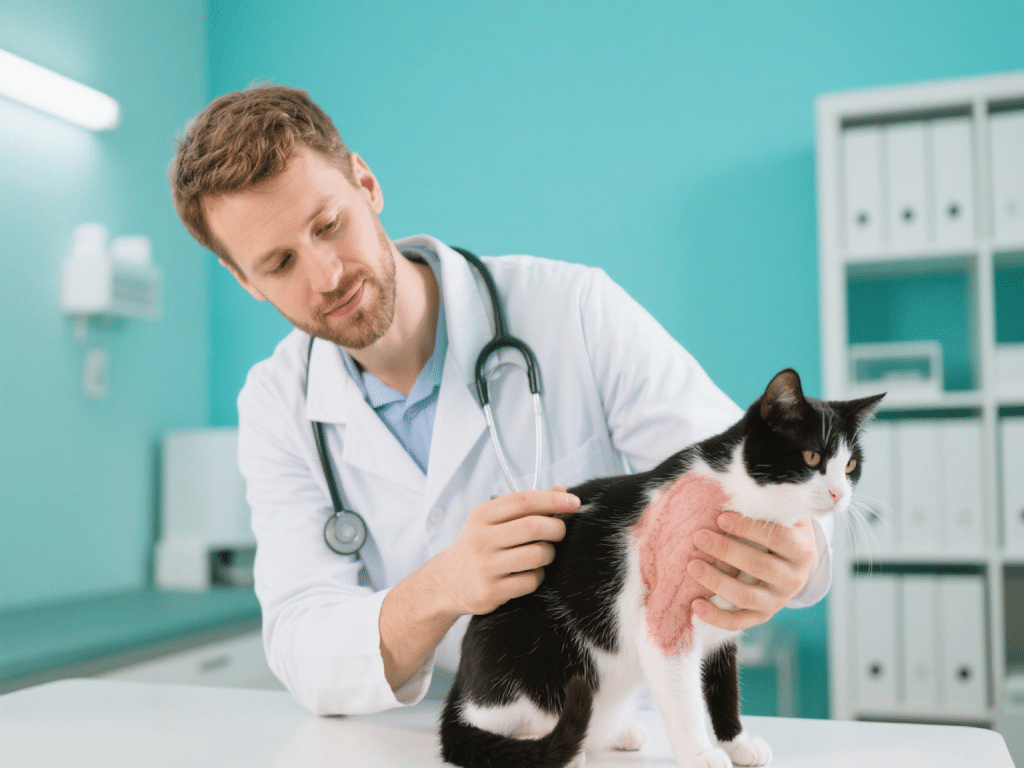
Understanding Flea Allergy Dermatitis in Cats: Prevention and Treatment Options
Flea allergy dermatitis (FAD) ranks as the most common itchy skin disease in cats. Even a single fle...
Read More →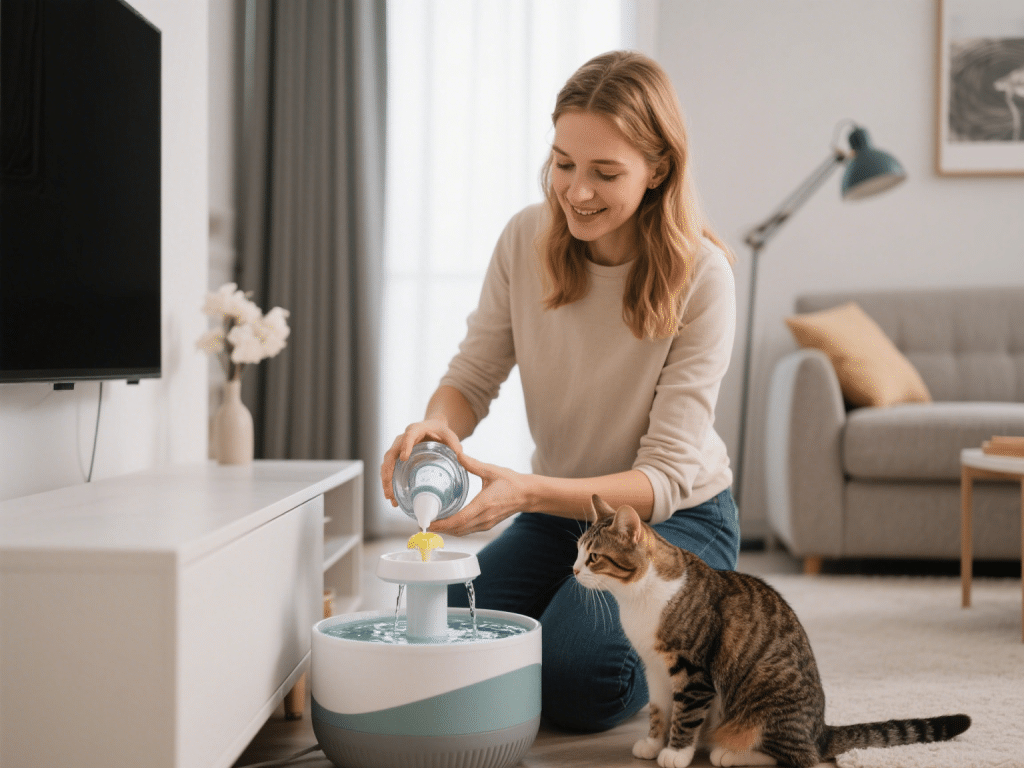
Best Water Fountains for Cats to Encourage Hydration
IntroductionDehydration in cats can lead to urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney disease, and bla...
Read More →
Tips for Managing Cat Shedding During the Summer Months
IntroductionAs temperatures rise, cats shed more to maintain ideal body temperature. While natural, ...
Read More →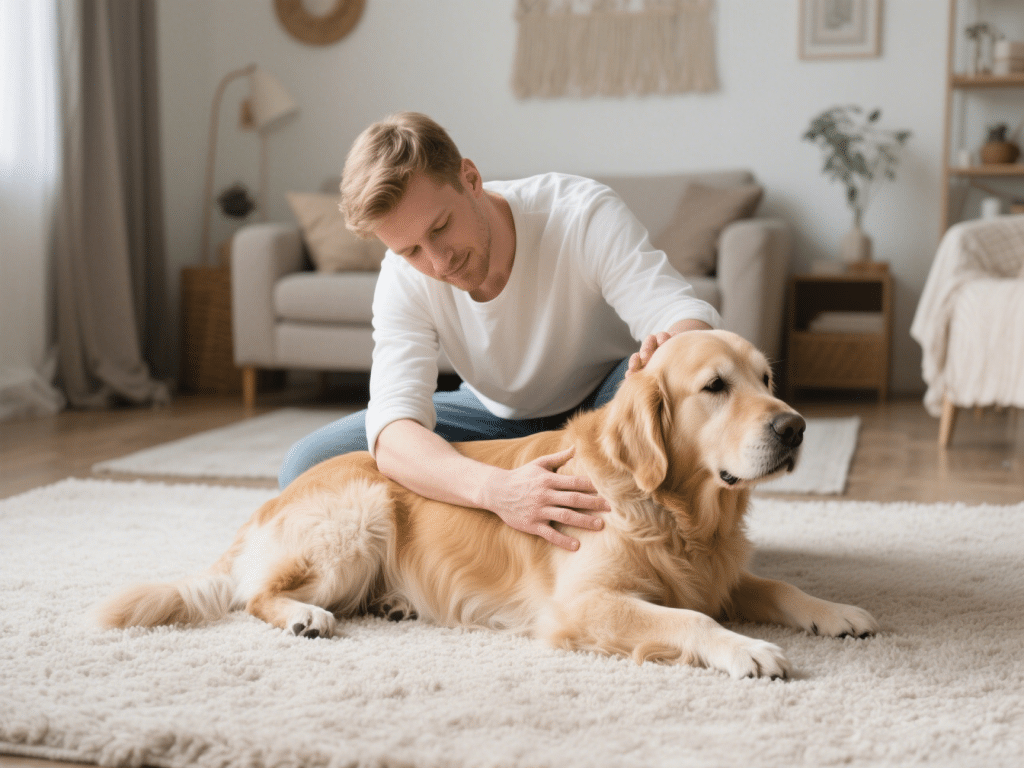
Pet Massage Basics: Relaxation Techniques for Cats and Dogs
IntroductionGentle massage promotes relaxation, improves blood flow, and strengthens the bond betwee...
Read More →
How to Introduce a New Pet to Your Home: Tips for a Smooth Transition
How to Introduce a New Pet to Your Home: A Stress-Reduction BlueprintBringing a new pet home is exci...
Read More →
Understanding Pet Health: Preventative Care and Regular Check-ups
Understanding Pet Health: Preventative Care and Regular Check-ups Are LifesaversOwning a pet brings ...
Read More →
The Best Diet for a Pet Raccoon
Raccoons make very interesting pets. They are curious, mischievous, playful, and get into everythin...
Read More →
Comments on "What to Expect in Dog Obedience Classes: A Complete Overview" :